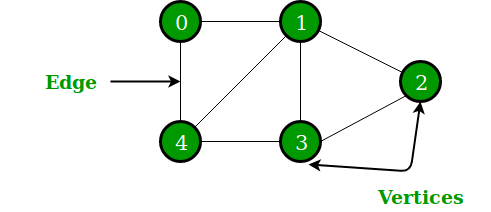
 Graph is a non-linear data structure like tree data structure. The limitation of tree is, it can only represent hierarchical data. For situations where nodes or vertices are randomly connected with each other other, we use Graph.
Graph is a non-linear data structure like tree data structure. The limitation of tree is, it can only represent hierarchical data. For situations where nodes or vertices are randomly connected with each other other, we use Graph. A graph data structure consists of a finite (and possibly mutable) set of vertices (also called nodes or points), together with a set of unordered pairs of these vertices for an undirected graph or a set of ordered pairs for a directed graph.
A graph data structure consists of a finite (and possibly mutable) set of vertices (also called nodes or points), together with a set of unordered pairs of these vertices for an undirected graph or a set of ordered pairs for a directed graph.